Lives Saved
Lives Saved
in
2023
- Deaths: Government of Canada
- Population: Government of Canada
Quick Links
- There were a total of 326,215 deaths in Canada in 2023
- 169,564 of all deaths were among males
- 1,514 of all deaths were among those aged 20-24
- 991 of all deaths were among men aged 20-24
991 deaths from All Causes were among men aged 20-24
2023 vs New Normal™ for men aged 20-24 in Canada
- 991 of 991 total deaths were from All Causes
- 100.00% of all deaths were from All Causes
- This is down 10% compared to Old Normal rates.
- 1,087 of 1,087 total deaths would have been expected under Old Normal conditions.
- 96 fewer than expected deaths from All Causes in 2023.
- 174 fewer than expected deaths from All Causes (2015-2023)
- To show this year’s deaths from All Causes are down 10% compared to Old Normal rates, we need to calculate the rates for both 2023 and for the Old Normal.
Remember, death rates are calculated to answer these questions:
- “How many men aged 20-24 were there?” and
- “How many of them died from All Causes?”
The following 2 charts provide this information:
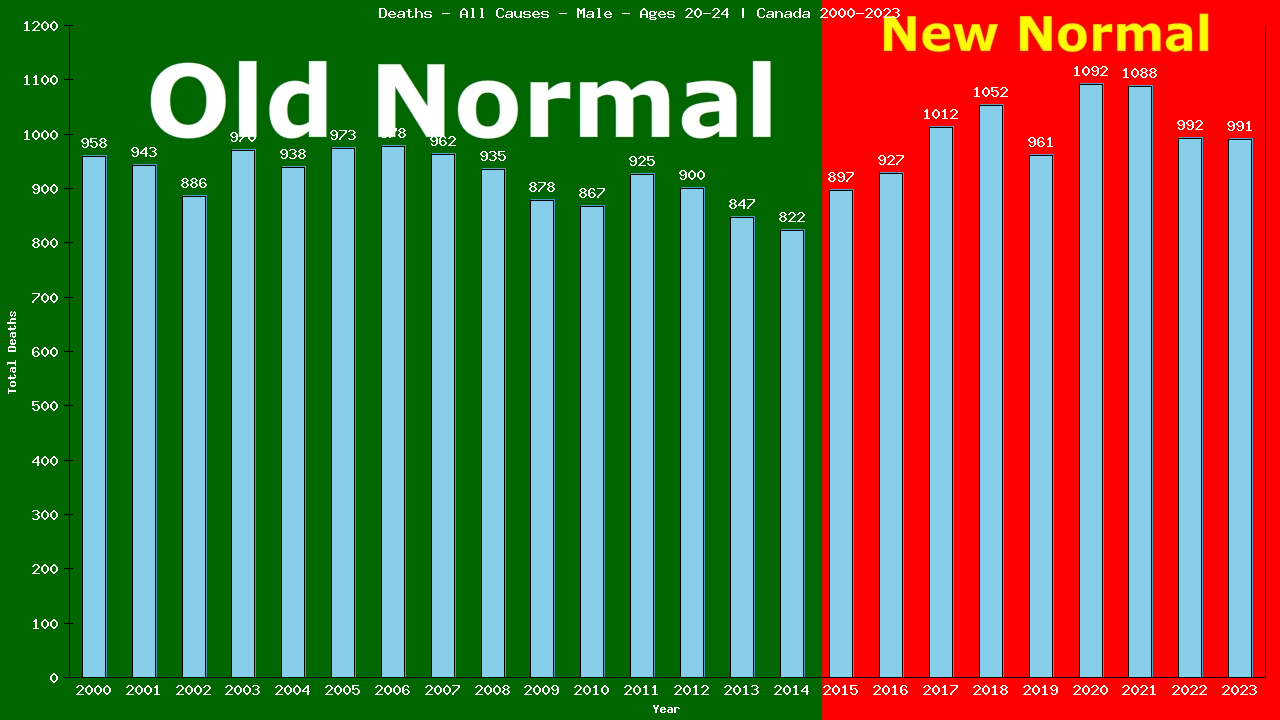
Deaths – All Causes – Male – Aged 20-24 | Canada, Canada

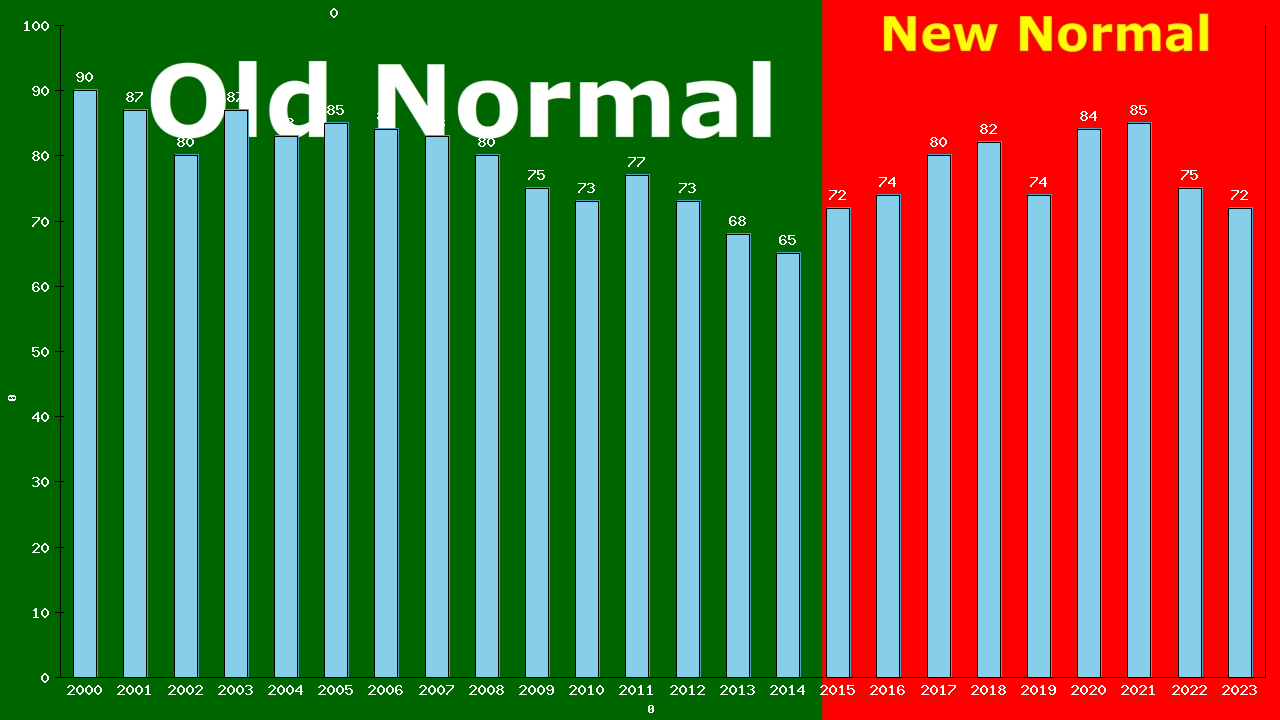
Population – Male – Aged 20-24 – [2000-2023] | Canada, Canada
![Graph showing Population - Male - Aged 20-24 - [2000-2023] | Canada, Canada](/wp-content/plugins/dfuc-display/charts/canada/canada/2023/all/Male/20-24-pop.png)
From the charts, we can see that in 2023, 991 of 1,366,446 men aged 20-24 living in Canada died from All Causes.
991 ÷ 1,366,446 = 0.00073 (2023 CDR)
Deaths/100,000 Male 20-24 from All Causes
The table shows there were a total of 13,782 deaths from All Causes among 17,332,503 men aged 20-24 living in Canada in the 15 years immediately prior to the New Normal™.
13,782 ÷ 17,332,503 = 0.00080 (Old Normal CDR)
We can use the Old Normal rate to predict this year’s deaths:
2023 pop X Old Normal CDR = expected deaths
1,366,446 X 0.00080 = 1,087 expected deaths
The difference between actual and expected deaths shows lives saved or lost:
991 – 1,087 = -96
Dividing the actual deaths by the expected deaths gives us the comparative rates:
991 ÷ 1,087 = 0.9007
This reveals 96 lives saved and is 90.07% of what we expected (a decrease of 10%) in deaths from All Causes among men aged 20-24 living in Canada in 2023, as compared to the Old Normal.
This is the same method used by Public Health to calculate the 5-yr CDR (Cumulative Death Rate):
8,021 ÷ 10,185,941 = 0.00079 (5-yr CDR)
1,366,446(2023 pop) X 0.00079 = 1,076 expected deaths
The difference between actual and expected deaths:
991 – 1,076 = -85 or 85 lives saved
Divide actual deaths by expected deaths:
991 ÷ 1,076 = 0.9094 or a decrease of 9%
for deaths from All Causes among men aged 20-24 living in Canada in 2023, as compared to the previous 5 years.
Compare our Old Normal to the 5yr CDR. Does it tell the same story your TV does?
Finally, the same method can also be used to compare our Old Normal rate to the New Normal™ rate:
New Normal™ population X Old Normal rate = expected deaths
11,552,387 X 0.00080 = 9,186 expected deaths
The difference between actual and expected deaths:
9012 – 9,186 = -174 or 174 lives saved
Dividing the actual deaths by the expected deaths:
9,012 ÷ 9,186 = 0.9689 or a decrease of 3%
in deaths from All Causes among men aged 20-24 living in Canada in the New Normal™, as compared to the Old Normal.
Justin Trudeau and his globalist buddies came up with UN “Sustainable” Development Goal SDG3 – “Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages” and began implementing it in 2015.
Browse through the tabs for all ages below to see the results of 9 years of their New Normal™
Is this health and well being?
Is this “sustainable”?
Can we allow this to continue?
The world has been led to believe that a deadly pandemic swept the globe beginning in 2020, causing an increase in death rates, especially among the elderly
The data show that death rates began to increase in 2015, immediately upon implementation of the UN’s 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, that young adults have experienced ever-increasing death rates since, and that death rates among the elderly have remained relatively stable.
Return to the top of the page to select another age category.
×









